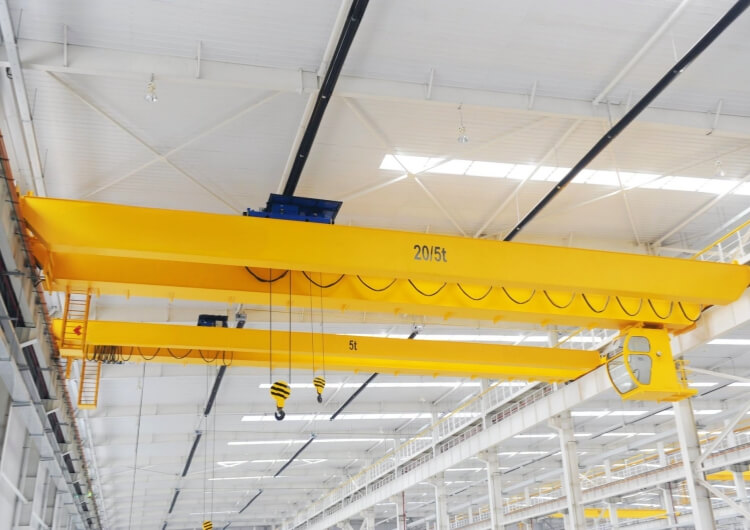
Overhead Cranes for the Aviation Industry: Hangar-Ready Solutions for Assembly, MRO, and Paint Shops
Aviation assembly lines and MRO (maintenance, repair, and overhaul) facilities demand lifting systems that combine precise positioning, strict safety controls, and zero-interference envelopes around large aircraft structures. This guide explains how to design and select overhead lifting solutions for final assembly, aircraft docking, engine handling, and paint hangars—with special focus on three deliverable options you can implement fast
1) Aviation Workflows & Typical Crane Tasks
1.1 Final Assembly / Structural Integration
Use cases: fuselage join, wing-to-body mating, landing gear install, interior modules.
Key needs: long travel with anti-sway, micro-speed hoisting, and safe “no-go” zones around wings and doors.
Recommended mix: a main bay low-headroom bridge for large modules, plus line-side jibs for fixtures, tools, and fasteners.
1.2 MRO Hangars
-
Use cases: heavy checks, component overhaul, structural repair.
-
Key needs: flexible coverage without interfering with tail/wing envelopes; frequent light lifts at workstations.
-
Recommended mix: LX low headroom bridge crane for major removals; jib cranes on columns for localized tasks.
1.3 Engine Handling & Powerplant Shops
-
Use cases: engine removal/installation (R/I), quick change, module swap, stand transfers.
-
Key needs: dual-hook coordination, fine positioning near engine pylons, controlled travel near nacelles.
-
Recommended mix: LX bridge (dual hoist/dual trolley when needed) + strategically placed jibs at build stands.
1.4 Paint Hangars & Surface Treatment
-
Use cases: strip, clean, mask, spray, cure.
-
Key needs: explosion protection for electricals, low-sparking components, paint-mist corrosion resistance, sealed electrics.
-
Recommended mix: certified explosion proof overhead cranes for any lifting inside paint/solvent zones; auxiliary jib cranes for tools and fixtures at docking platforms.
2) Why Low Headroom Bridges Are a Game Changer in Hangars

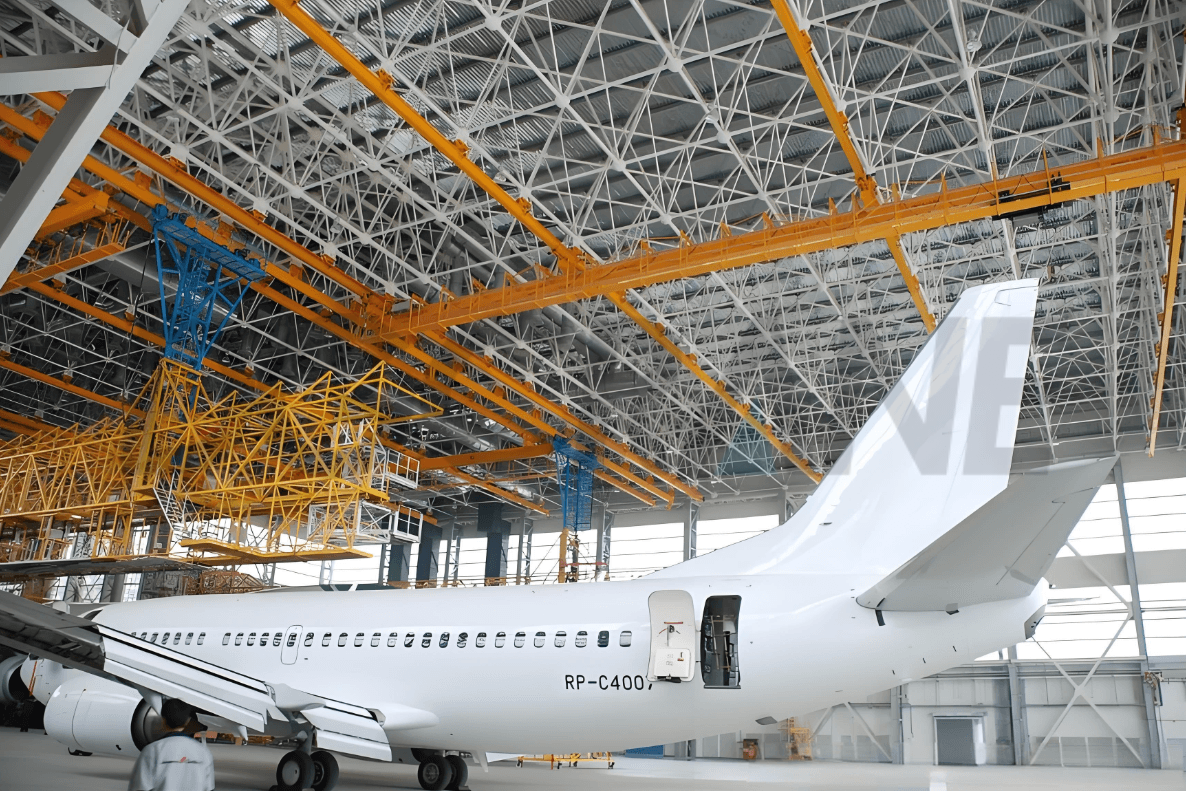
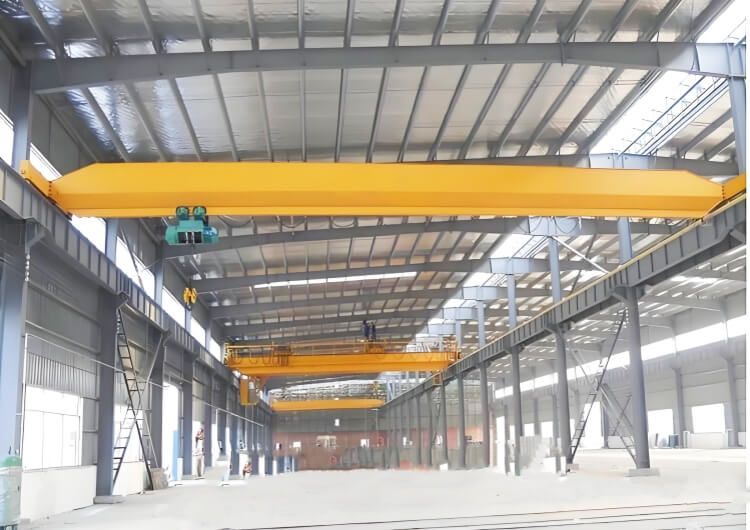
Retrofit hangars often have limited top-of-rail to roof truss clearance. Conventional bridges lose too much hook height, forcing costly steel or roof changes. An LX low headroom single girder configuration places the hoist in a side-mounted or integrated trolley arrangement to maximize hook approach and hook height without major civil works.
-
Benefits in aviation use:
-
More hook height under existing trusses/MEP without raising the roof.
-
Tighter end approaches to get closer to fuselage stations and docking platforms.
-
Lower wheel loads vs. heavier double-girder designs in some spans.
-
Implementation path: evaluate existing truss drawings, HVAC/lighting interference, door heights, and wing/tail envelopes; then size an LX solution for the required hook path and safe approach.
→ Learn more: Low Headroom Solution (LX)
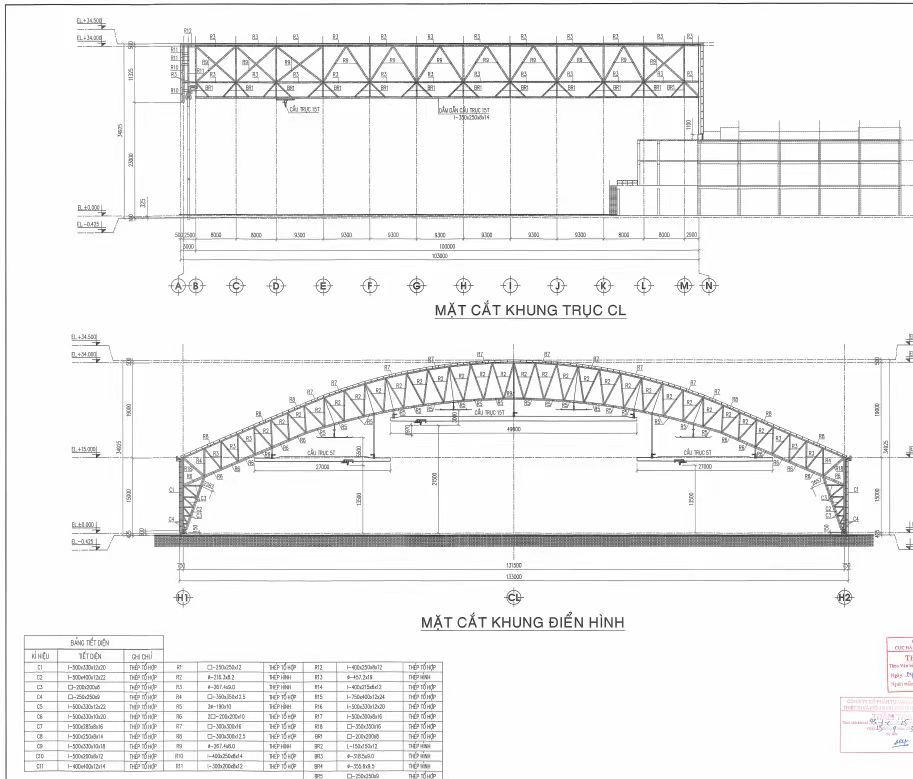
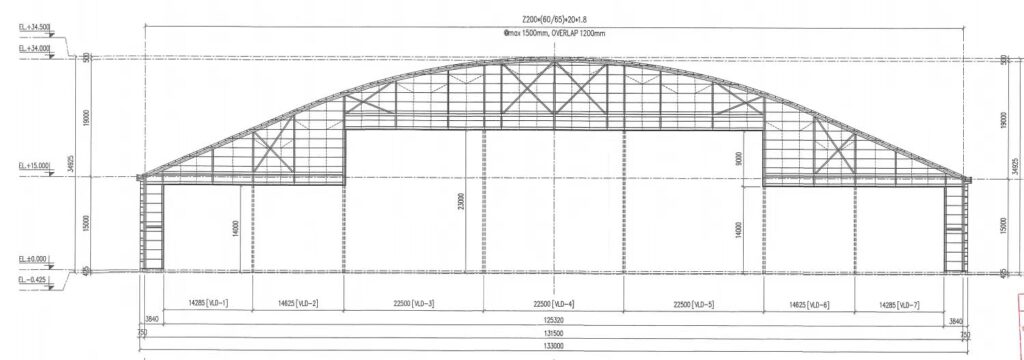
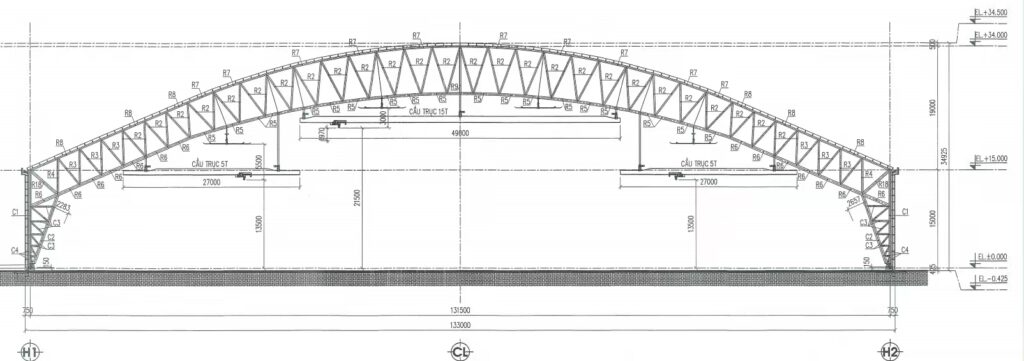
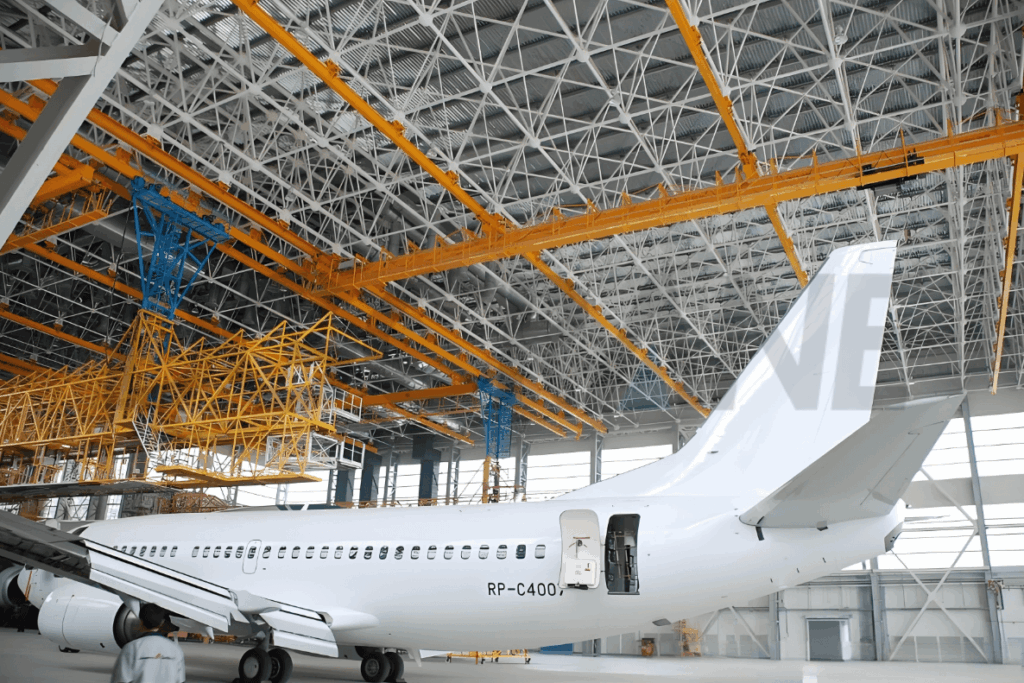
3) Explosion Proof for Paint Hangars: What Matters
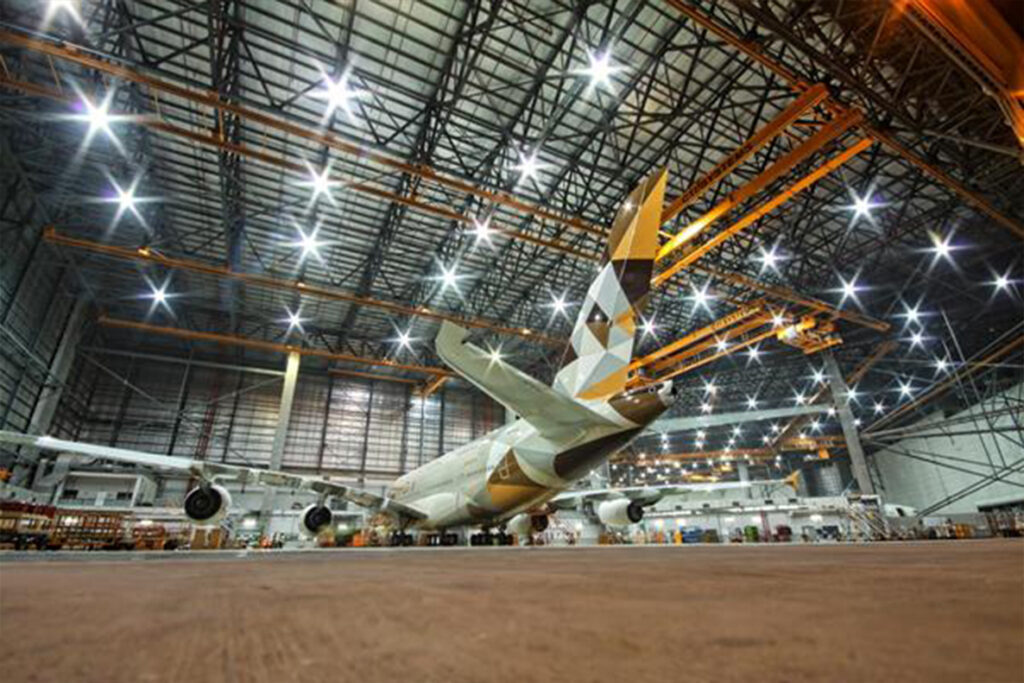

Paint hangars present flammable vapors, conductive mists, and cleaning solvents. Your lifting gear must prevent ignition and resist contamination:
Explosion-proof electrics (motors, brakes, enclosures) matched to the hazard area classification.
Antistatic measures and effective earthing for moving equipment.
Corrosion-resistant finishes and sealed cable management against paint fog.
Low-spark running gear (polymer/PU wheels where suitable) and protected control circuits.
Operational interlocks: slow zones, soft limits, and maintenance lockout to protect workers at docking platforms.
For any lifting inside paint shops or solvent rooms, specify a certified explosion-proof overhead crane with documented testing and inspection routines.
→ See: Explosion-Proof Overhead Cranes
4) Jib Cranes Along the Aircraft Docking Line
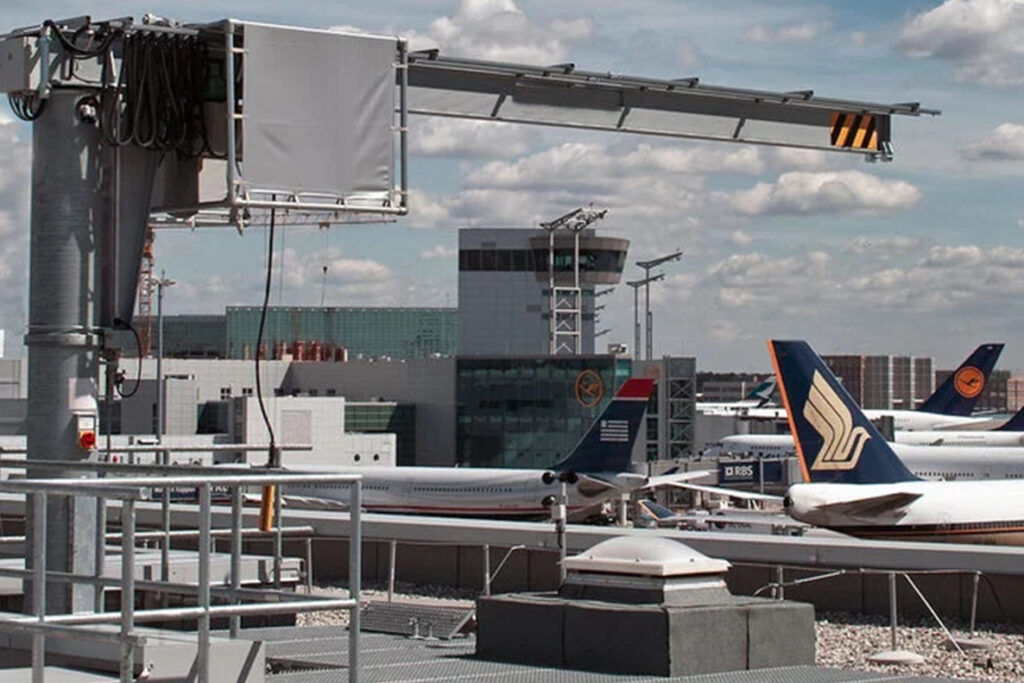

Jib cranes shine in cell-based and line-side work: they bring tools, composites, rivet guns, fasteners, panels, and small subassemblies exactly where mechanics need them—without tying up the main bridge crane.
Why jibs help aviation teams
Short, frequent lifts close to the task—reduce waiting time for the main crane.
360° or defined-arc coverage around docking stations.
Lower installed cost per workstation; easy to reconfigure with process changes.
Place jibs at high-traffic bays (doors, wing roots, interior fit-out areas) to shorten takt times.
→ Explore options: Jib Cranes
5) Controls, Safety, and Digital Functions to Specify
Anti-sway with micro-speed: smoother lifts near sensitive skins and windows; less rework.
Dual-hook coordination (or dual trolley): synchronized hoisting for engines/large panels.
Zoning & soft-limits: define slow zones near wings, doors, jetways, and docking platforms.
Collision avoidance: crane-to-crane, crane-to-structure, and personnel proximity alerts.
Condition-based maintenance: hoist run-time, overload counts, brake cycles; predictive alerts minimize AOG risk.
Traceable operations: data logging for QA and incident review in regulated facilities.
6) Material & Protection Choices for Hangar Environments
-
Paint-mist / solvent exposure: sealed electrics, coated metals, stainless fasteners in critical areas.
-
Humidity / coastal locations: anti-corrosion systems and closed cable carriers.
-
Clean zones / composites: low-dust components, smooth finishes, drip-free lubrication.
7) Retrofit Playbook (Fast Path to ROI)
-
Survey: roof truss, door headroom, HVAC/MEP, docking geometry, wing/tail envelopes.
-
Define hook paths: max dimensions for engines, landing gear, interiors; include tooling weights.
-
Choose system mix:
-
Main bay → LX low-headroom bridge;
-
Paint area → Explosion-proof overhead crane;
-
Workstations → Jib cranes at takt-critical positions.
-
-
Controls matrix: anti-sway, dual-hook sync, zoning, speed limits, and interlocks.
-
Execution: phased install during planned downtime; SAT with lift plans and operator training.
-
Sustain: digital inspections, spares, and CBM analytics to prevent AOG.
8) Typical Specification Snapshot (to start RFQ)
Loads: engine module 8–15 t; landing gear 5–12 t; interiors 1–3 t; tooling 0.5–2 t.
Duty: frequent starts/stops; specify appropriate FEM/ISO duty class.
Speed ranges: main hoist with micro-speed; travel with soft acceleration; slow zones at docking.
Power & controls: radio remote + pendant backup; safe e-stops; lockout/tagout points.
Compliance: explosion-proof only where required (paint/solvent zones); hangar-safe components elsewhere.
(Values above are indicative starting points for scoping and can be refined after we review your hangar drawings and process weights.)

Expert in Overhead Crane/Gantry Crane/Jib Crane/Crane Parts Solutions
Eileen
With 20+ years of experience in the Crane Overseas Export Industry, helped 10,000+ customers with their pre-sales questions and concerns, if you have any related needs, please feel free to contact me!
FAQs
Yes—use a low headroom single girder configuration to recover hook height and end approaches without civil changes. See our Low Headroom Solution (LX).
No. Only paint/solvent-exposed zones typically require explosion-proof equipment. Elsewhere, standard hangar-grade protection is sufficient. For paint shops, specify certified systems: Explosion Proof Overhead Cranes.
At line-side stations with frequent light lifts—doors, wing roots, interiors, and engine build stands. Details: Jib Cranes.
Yes—dual-hook or dual-trolley synchronization with anti-sway and micro-speed improves accuracy and safety around nacelles and pylons.
We combine soft-limits, slow zones, anti-sway, and collision avoidance, plus tailored lift plans and operator training.
Latest Blog
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua
Overhead Cranes for the Aviation Industry | SLKJCrane
Overhead Cranes for the Aviation Industry: Hangar-Ready Solutions for Assembly, MRO, and Paint Shops Aviation assembly lines and
Intermodal Gantry Cranes (RMG & RTG) — Engineering Playbook
Intermodal Gantry Cranes (RMG & RTG) — Engineering Playbook This engineering-oriented guide targets rail-to-truck operations, inland ports (ICDs),
Electric Hoist Gantry Crane: Complete Sizing & Selection Guide | SLKJCrane
Electric Hoist Gantry Crane: A Complete Sizing & Selection Guide Choosing the right electric hoist gantry crane comes
MG Double Girder Gantry Crane with Hook | Heavy-Duty Outdoor Lifting
MG Double Girder Gantry Crane with Hook: Structure, Specs & Applications An MG double girder gantry crane with
Contact Us Now
Have questions about our cranes or need help?
Reach out to our friendly team for expert support and guidance.
We are here to help you power your journey towards a greener future !
Address: Crane Industry Park, Xinxiang City Henan Provice







